 Home > Turbocharger Failure Diagnosis
Home > Turbocharger Failure DiagnosisTurbocharger Failure Diagnosis

Loud whining noise, Loss of power, excess smoke, high fuel consumption, overheating, high exhaust temperatures and oil leakages from the turbocharger are all symptoms that could indicate turbocharger malfunction. However, these faults are often wrongly attributed to the turbocharger because defects in other components can produce the same symptoms. The turbocharger performance can only be impaired by mechanical damage or blockage caused by dirt.
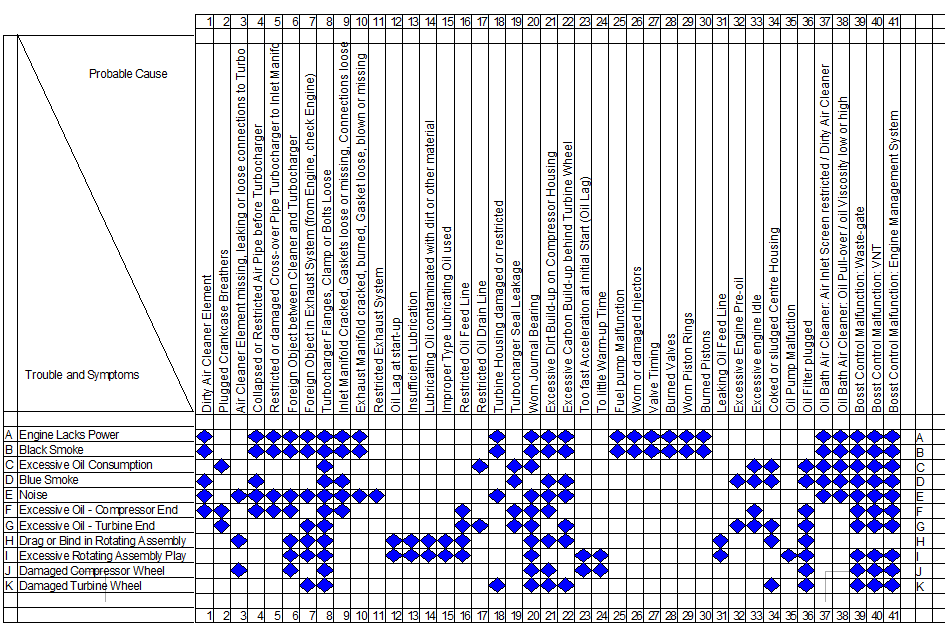
This trouble-shooting chart provides a comprehensive list of the most common symptoms related to turbocharger failure. Before turbocharger removal, verify the problem by consulting the chart below.
Most turbocharger failures are caused by one of the four basic reasons:
- Lack of Lubrication - Contaminated Lubrication
- Foreign Object Damage - Overspeeding
1) Lack of Lubrication
· Low engine oil levels
· Obstructions in oil feed lines
· Build up of burnt oil in center housing
· Excessive Temperature
· Inferior oil quality.


2) Contaminated Oil
· Saturated oil filter
· Recycled Oil
· A rebuilt engine with impurities within the oil passages.
· Burnt oil from high temperatures.
· Residue from incomplete combustion.


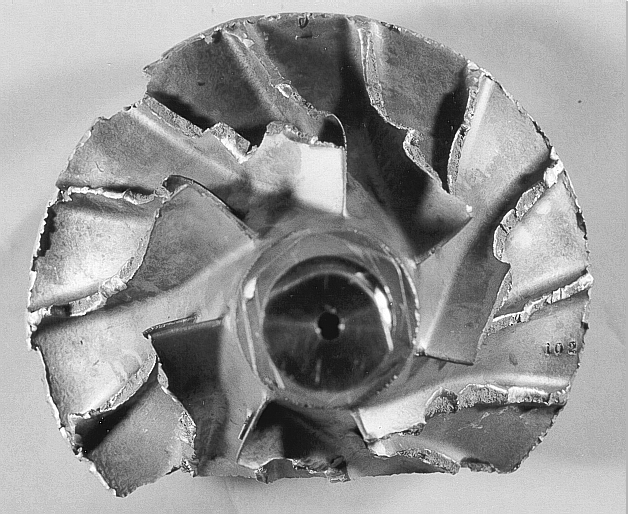
3) Foreign Object Damage
· Dirty or ripped air filter
· Fractured air intake hose
· Engine failure (metal object)
· Broken rings, valve failure and others


4) Overspeeding
· A badly ‘chipped/remapped’ or ‘over fuelled’ engine that isn’t to standard specification
· Incorrect volume of air in the turbo
· Worn injectors,
· Loss of signal to the Simple Rotary Electronic Actuator for the wastegate
· Fitting the incorrect turbo.
· The pneumatic or electric control is defective or leaking.

If you need help, please do not hesitate to contact us.